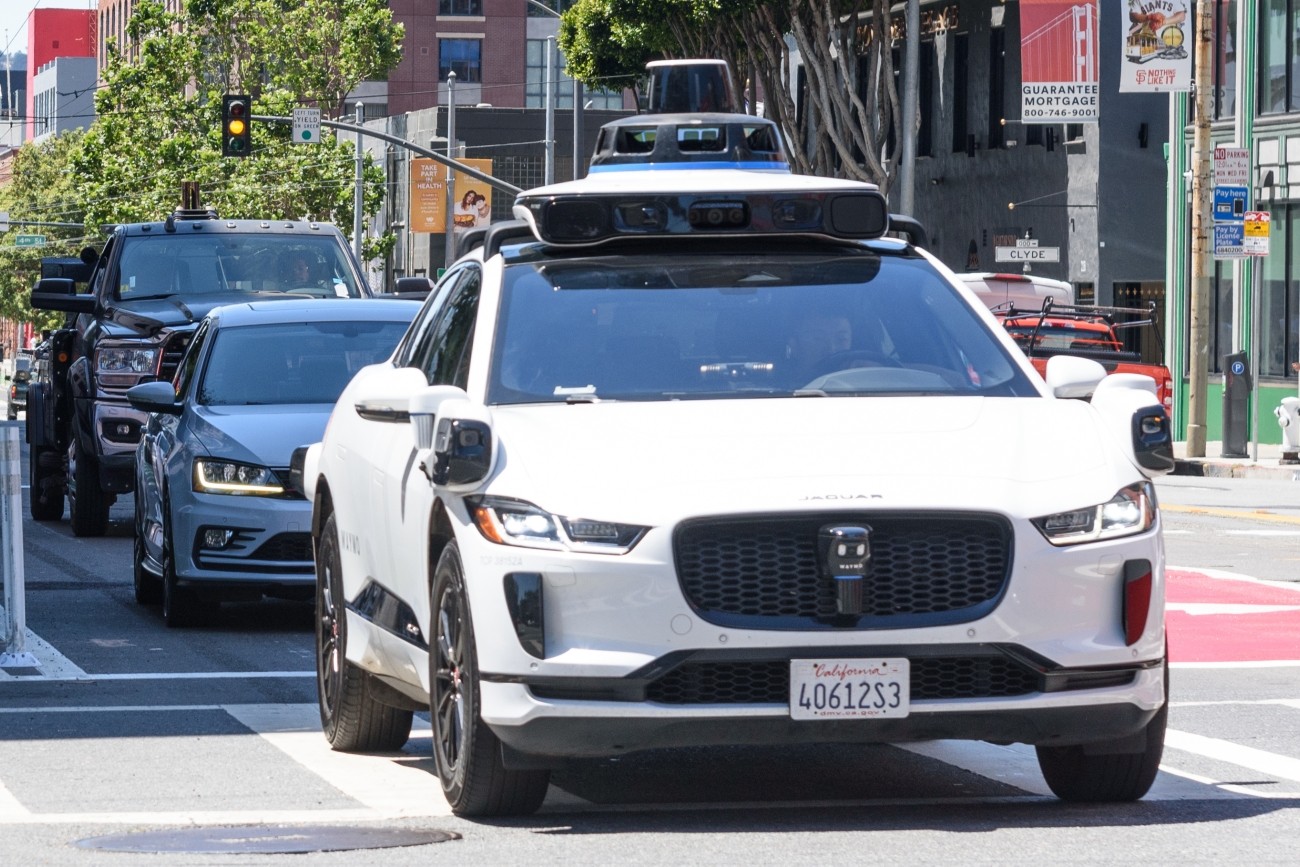
Autonomous Vehicle Services | Tesla, Cruise, EasyMile, Waymo, Zoox According to the UK Department of Transport, “a fully autonomous vehicle (AV) is capable of completing journeys safely and efficiently, without a driver, in all normally encountered traffic, road and weather conditions. In other words, AVs need to operate on par or better than human-driven vehicles in all conditions. AVs have the potential to drastically change our infrastructure, traffic and parking needs, insurance policies, and much more. AVs are continually growing in a number of markets, including car share and ridesourcing fleets (TNCs), shuttle services and personal vehicles. |
Ridesharing/Carpool | Scoop, Waze Carpool Ridesharing is the third-party service of matching riders and drivers with similar shared destinations, enabling them to split the cost of the ride. Unlike ridesourcing and ridesplitting, the driver is not fare-motivated. There are two types of emerging mobility ridesharing services: dynamic matching, which is the matching of riders to drivers on-demand, and the batching of matches, where travelers enter their desired pickup and drop-off schedule and all of the inputs are matched at a certain hour every day, alerting the users of their upcoming schedule. |
Microtransit/Shuttle services | Microtransit is a privately operated shuttle service, usually enabled by technology to operate along a dynamically generated route. Microtransit typically operates in areas where public transit is reaching capacity, not always available, or where there is significant demand for an alternative to public transit. As such, microtransit services usually focus on commuters’ experience and offer bus-stop similar service to individuals willing to pay the additional price above public transit. Microtransit companies can vary by fleet (buses or vans), route structure (fixed or dynamic), and, more recently, fleet ownership. |
Bike share/E-Bike | Ford GoBike, LimeBike, JUMP, Lyft Bike sharing is a system that makes bicycles available to users to access as needed for point-to-point or round-trip trips, traditionally to station kiosks. They are generally unattended and established in dense urban areas. Advances in bike share locking technology have allowed for free-floating or "dockless" bikes within a geographic region. Bike sharing can be privately owned, public, or, most commonly, offered through a public-private partnership. |
Courier Network Services | Doordash, Postmates, Grubhub, Caviar Courier Network Services are companies that develop a platform to connect orders to delivery drivers utilizing their app network. These on-demand delivery platforms connect thousands of part-time local delivery drivers with customers requesting products to be delivered immediately. |
Electric Moped Share | Scoot Scooter sharing is the shared-use of a fleet of mopeds, typically managed by a third-party. The mopeds are often electric. Systems usually allow for both point-to-point and round trips. Members can rent the mopeds by the minute. |
Ridesourcing/
Ride-hailing | Uber, Lyft Ridesourcing services match riders with drivers, on-demand. Ridesourcing is often referred to as “ridesharing”; however, we have chosen the term “ridesourcing” to distinguish the fact that these drivers do not share a destination with their fares. Ridesourcing companies are distinguished from taxi services by the ability to street hail (ridesourcing companies can only pick up pre-arranged rides). The companies are known in California as Transportation Network Companies (TNCs) and are regulated by the California Public Utilities Commission. |
Car share | GIG Carshare, Maven, Zipcar, car2go Point-to-point/One-way: Users can pick-up and drop off cars anywhere within a defined geographic region. The cars are stored on the street. This is the fastest growing model of car sharing. Point-to-point car sharing is typically managed by a third party who owns the fleet. Unlike other models of car sharing, point-to-point fares can be charged by the minute. At present, there are no point-to-point car sharing models in San Francisco. Round-trip: Users reserve a vehicle from the same pick-up spot they return the vehicle to. Vehicles are stored in parking lots and garages, though some cities have explored designated on-streetspaces, where car sharing vehicles are not subject to typical street parking violations, such as street cleaning. Round-trip car sharing is typically managed by a third party who owns the fleet and the fares are usually by the half-hour. |
Electric Standing Scooters/E-scooters | JUMP, Lime, Skip, Lyft, Scoot, Spin, Bird Scooter sharing is the shared-use of a fleet of scooters, typically managed by a third-party. The scooters are often electric. Systems allow for point-to-point trips. Members can rent the scooters by the minute. |